 | Ellensburg, Kittitas County, Washington, USA |
 |
GEOLOGY
Teanaway Basalt - Whole-rock K-Ar ages range from 39 to 47 Ma (Clayton, 1973). The name Teanaway basalt is used for the basaltic and andesitic rocks, and pyroclastic material north of Cle Elum and Ellensburg. The basalts are glassy to very fine-grained black rock containing numerous amygdules. Chalcedony can be found as amygdules and as fracture-fillings within the basalt or as sub-rounded clasts in glacial drift sediments of the area. These clasts are locally derived from the Teanaway basalt.
Different color varieties of chalcedony can be found in this region. The highly sought after corn-flower blue variety (Ellensburg Blue agate) has only been found loose in the soil associated with a Quaternary landslide deposit and has not been found in-place within outcrops of Teanaway basalt.
Watch Central Washington University geology professor Nick Zentner's YouTube video - Ellensburg Blue Agates: Downtown Geology Lecture Series for a very informative video discussing the geologic context for the formation and deposition of the Ellensburg blue agates.
MINERALS
| SiO2 - Occurs as agate in various colors, often banded. Ellensburg blue - blue variety, carnelian - red/orange variety, and white/grey agates can be found. Agate interiors are often botryoidal and/or are lined with crystalline quartz. Crystals range in size from drusy to about 2 cm. Crystalline quartz is clear to slightly amethyst. |

polished QUARTZ, var. blue chalcedony |

polished QUARTZ, var. banded blue chalcedony "Ellensburg blue" |
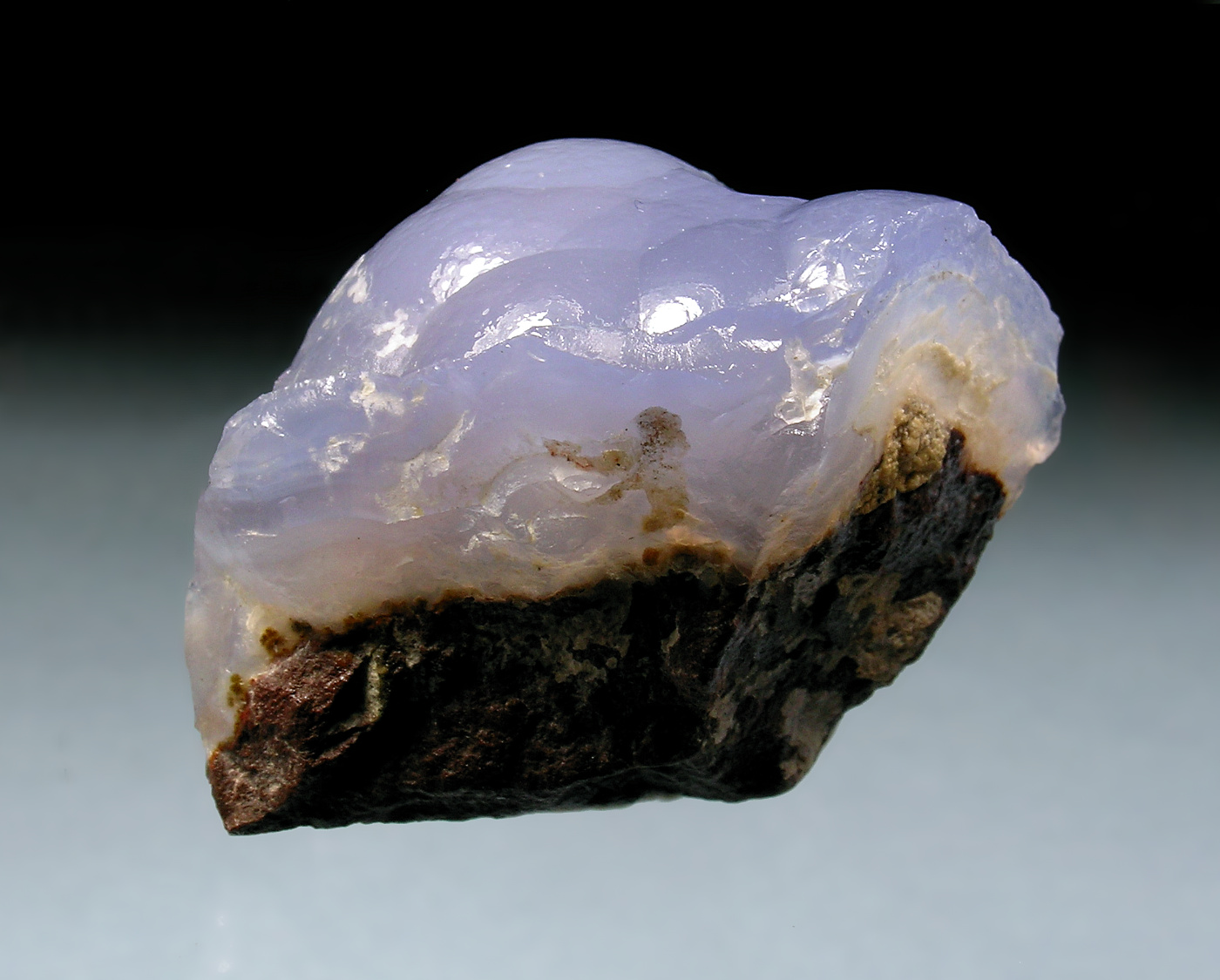

polished QUARTZ, botryoidal blue chalcedony "Ellensburg blue" |
Clayton, D. N., (1973) Volcanic history of the Teanaway Basalt, east-central Cascade Mountains, Washington: Washington University, Seattle, M. S. thesis, 55 p.